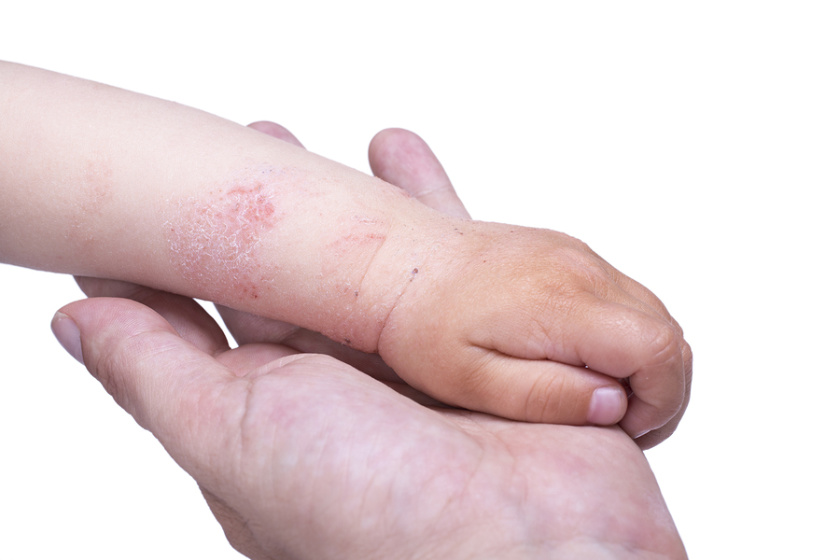
About one third of children who have moderate to severe eczema also have a food allergy. So, what is the link between these two conditions? First, let’s learn more about them.
What is eczema?
Eczema is a skin condition, which causes red, itchy areas on the skin. Scratching can cause the skin to break, ooze and then crust over.
Eczema is more common in children than adults. Some children outgrow it, but it can also return later in life.
What is a food allergy?
A food allergy is when the body’s immune system thinks a food protein (like nuts, soy or milk) is harmful. This causes the body to have symptoms of an allergic reaction like:
-
Flushed face, hives or a rash, red and itchy skin
-
Swelling of the eyes, face, lips, throat and tongue
-
Trouble breathing, speaking or swallowing
-
Cramps, diarrhea, vomiting
Food allergies are more common in children than adults. Children can outgrow some food allergies.
Does eczema cause food allergies?
Eczema increases the chance of developing a food allergy. If your child’s scratched open skin is in direct contact with a food allergen, such as peanuts, the food allergen can get into the body more easily and may cause the immune system to react.
Keeping eczema under control may help prevent food allergies because healthy skin will help stop food allergens from getting into the body.
Does having a food allergy cause eczema?
No. Food allergies do not normally cause eczema. Food allergies and eczema are two separate conditions. However, food allergies are more common in children who also have eczema.
Bottom line
Eczema can increase the chance that a food allergy develops. However, a food allergy does not cause eczema.
Eczema cannot be cured, but it can be managed. Talk to your health care provider for advice if your baby has eczema.
You may also be interested in:
Food Allergies and Babies
Food Allergies and Intolerance
Last Update – April 26, 2018